June 16, 2024 By Usman Ahmed 12 minutes read

An AC motor is a type of electric motor that runs on alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity changes direction periodically, unlike the direct current (DC) that flows in one direction. AC motors are incredibly important because they power a wide variety of machines and devices both in industries and at home.
Important feature of AC motors is their efficiency. Efficiency means how well something uses energy. AC motors are designed to use electricity very effectively, which helps save energy and reduce costs.
In industries, AC motors are used to operate heavy machinery like conveyor belts, pumps, and fans. At home, AC motors are found in many common appliances. For example, the motor in your refrigerator keeps your food cold. In this article we will discuss in detail about types of Ac motors used in industry.
An AC motor has two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor, and it has coils of wire that create a magnetic field when AC electricity flows through them. The rotor is the part that moves and is placed inside the stator.
When the AC electricity flows through the stator, it creates a rotating magnetic field. This rotating field interacts with the rotor, causing it to turn and produce mechanical motion. This motion can then be used to power various machines and devices.

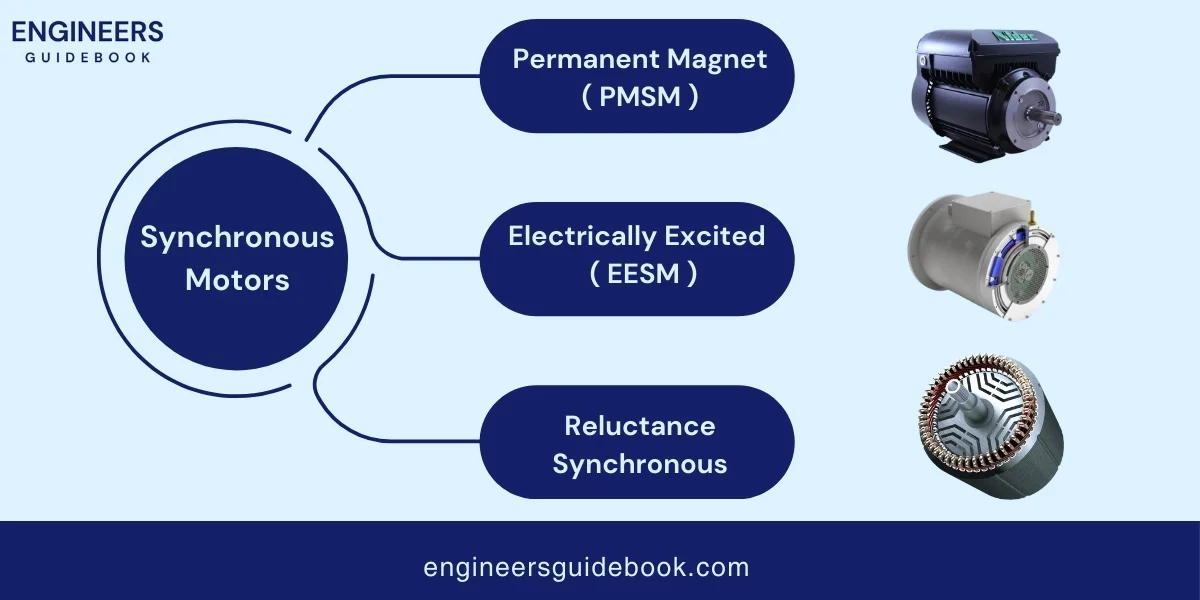
A synchronous motor works by matching its speed with the frequency of the supply current. This means if the supply current changes its direction 60 times a second (which is common in many places), the motor also changes direction 60 times a second. This matching of speeds is called synchronization.

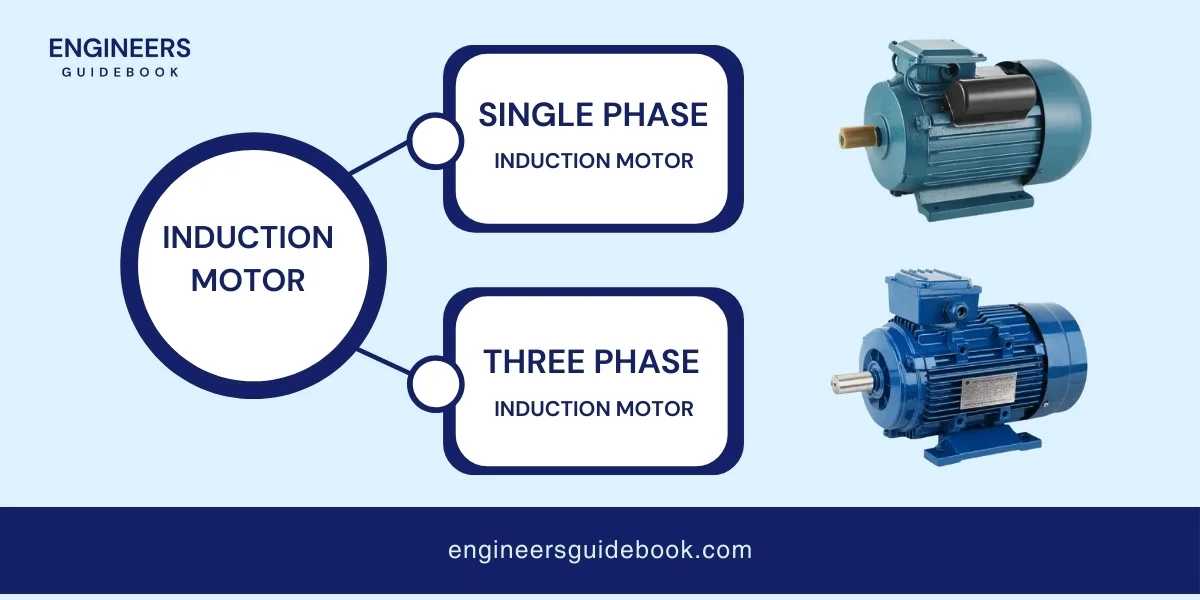
An induction motor is an electric motor that uses electromagnetic induction to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
An induction motor has two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part that creates a rotating magnetic field when electricity flows through it.
The rotor is the moving part that is placed inside the stator. When the magnetic field from the stator passes over the rotor, it induces (creates) a current in the rotor.
This induced current creates its magnetic field, which interacts with the stator’s field, causing the rotor to turn and produce mechanical motion.

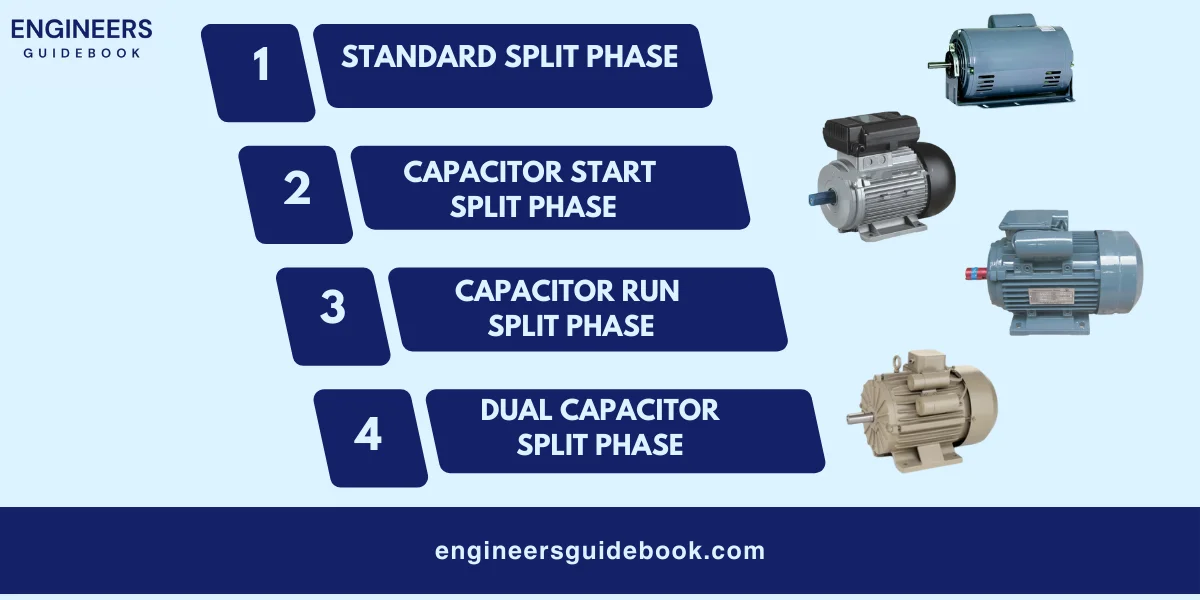
A split-phase motor is a type of single-phase induction motor that uses two windings to start and run.
These windings are called the start winding and the run winding. When the motor is turned on, both windings are energized.
The start winding is placed at an angle to the run winding, creating a phase difference between the two. This phase difference generates a rotating magnetic field that starts the motor.
Once the motor reaches a certain speed, a centrifugal switch disconnects the start winding, and the motor continues to run on the run winding.
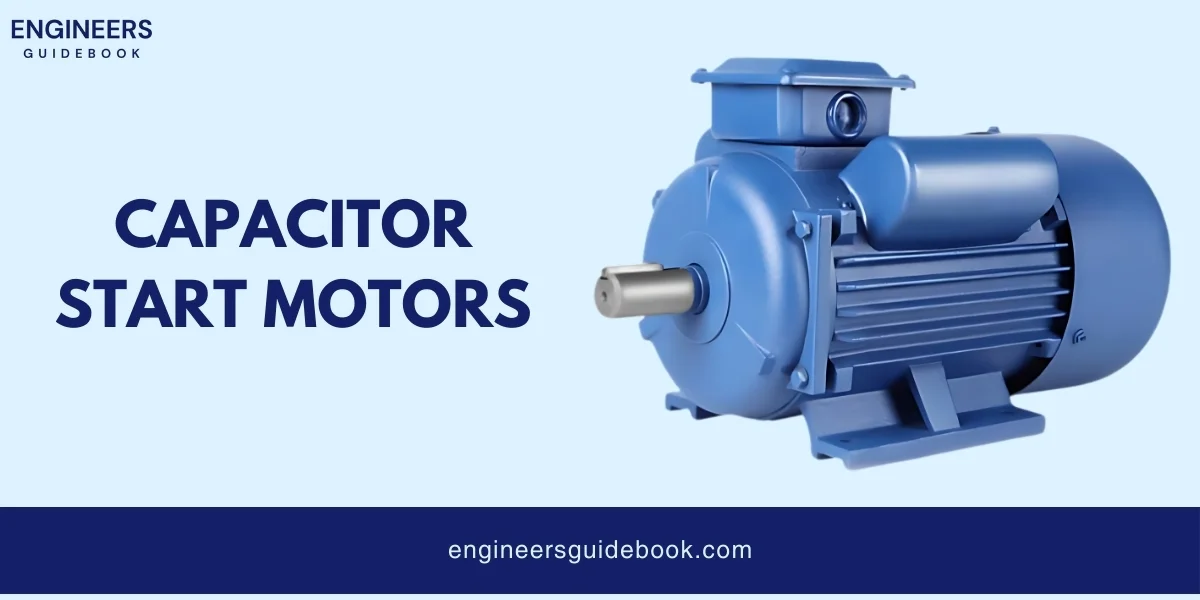
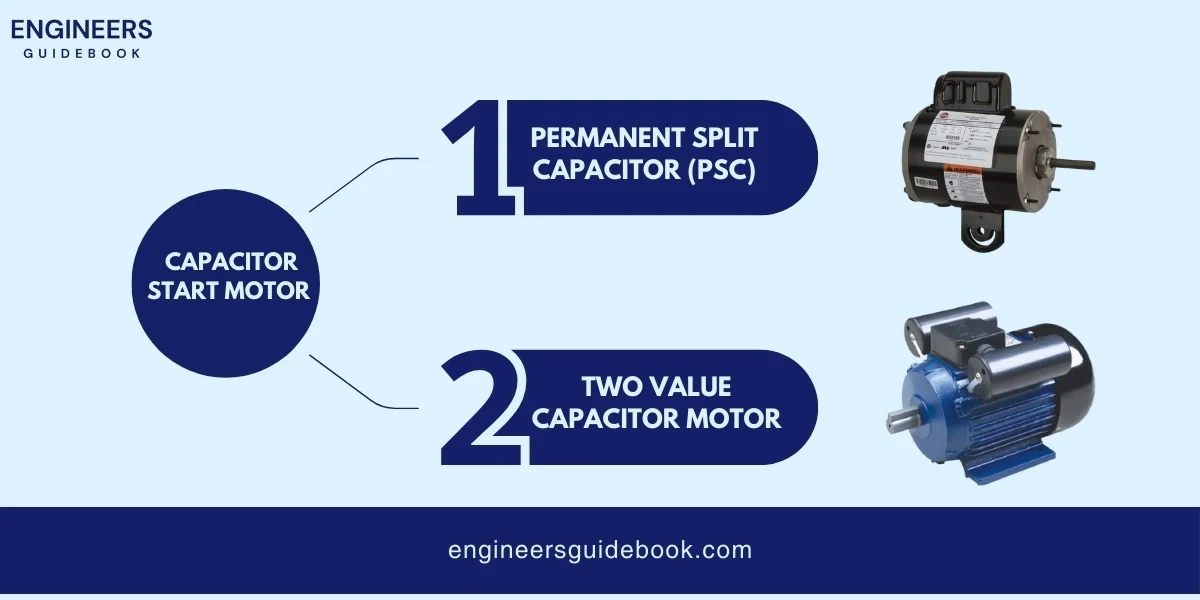
A capacitor-start motor is a type of AC motor that uses a capacitor to improve its starting performance.
This motor has two windings: a start winding and a run winding. The capacitor is connected in series with the start winding.
When the motor is turned on, the capacitor creates a phase difference between the start and run winding current.
This phase difference generates a strong starting torque, which helps the motor start quickly.
Once the motor reaches a certain speed, a centrifugal switch disconnects the start winding and the capacitor, and the motor continues running on the run winding alone.
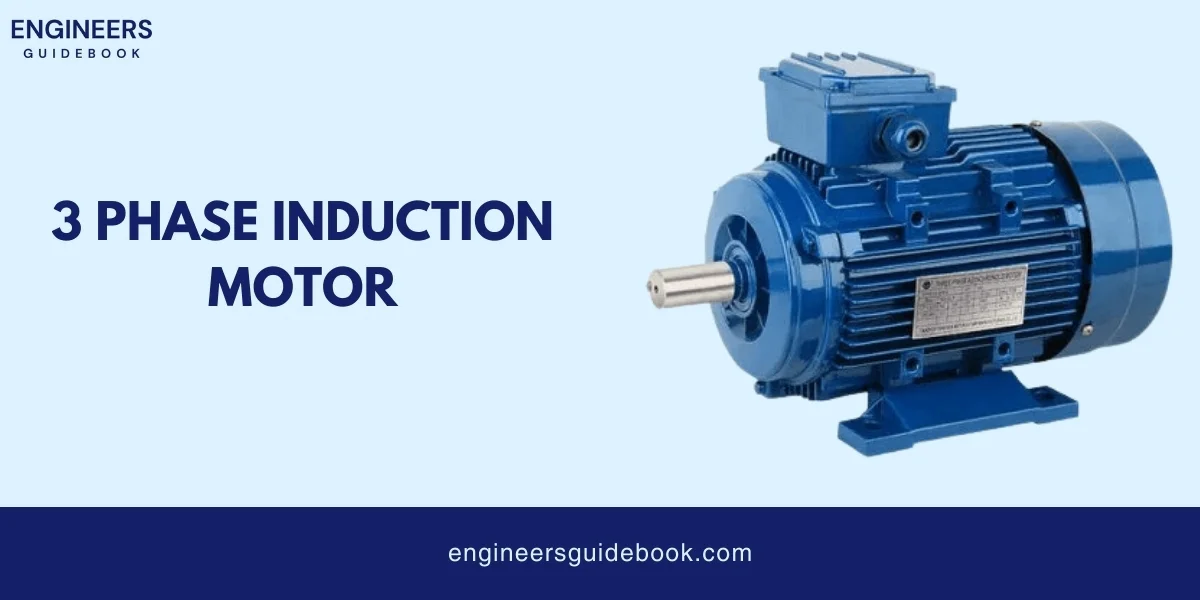
A three-phase induction motor is an electric motor that produces motion using three-phase alternating current (AC).
It has two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part and contains coils arranged in three sets, each connected to a different phase of the AC power supply.
When electricity flows through these coils, it creates a rotating magnetic field. This field induces a current in the rotor, which causes it to turn and generate mechanical motion.

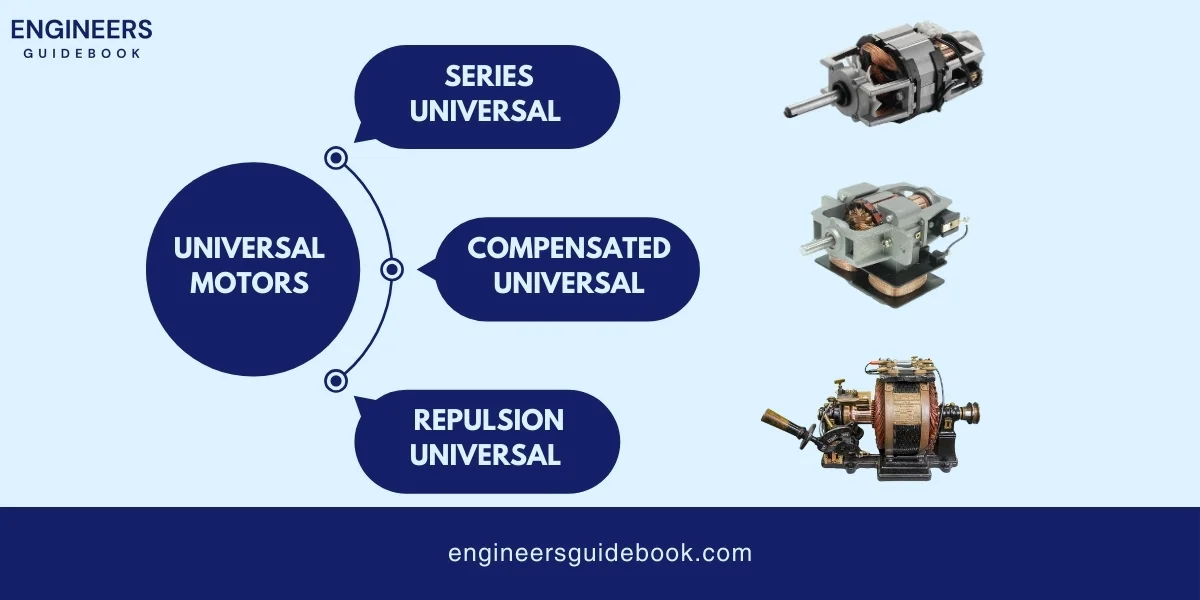
A universal motor is a type of electric motor that can run on either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC).
This motor has a stator (the stationary part) and a rotor (the rotating part) like other motors. What makes it unique is the way it uses both AC and DC power.
It has a series winding, meaning the field coils and the armature (the part of the motor that spins) are connected in series.
When electricity flows through the motor, it creates a magnetic field in the stator, which interacts with the magnetic field in the rotor, causing the rotor to spin and generate mechanical motion.

A servo motor is a special type of motor used for precise control of position, speed, and acceleration.
It consists of a regular motor coupled with a sensor for position feedback. This motor is controlled by a signal (called a pulse-width modulation signal, or PWM) that tells it how far to move.
The servo motor can move to a specific position and hold that position, which makes it very useful in many applications.
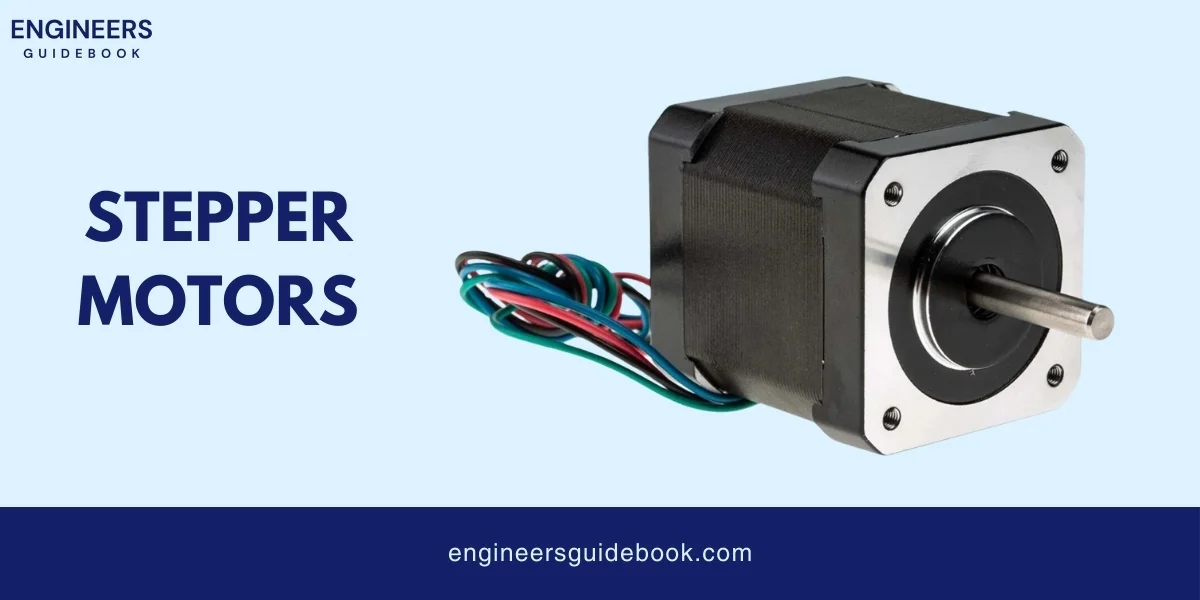
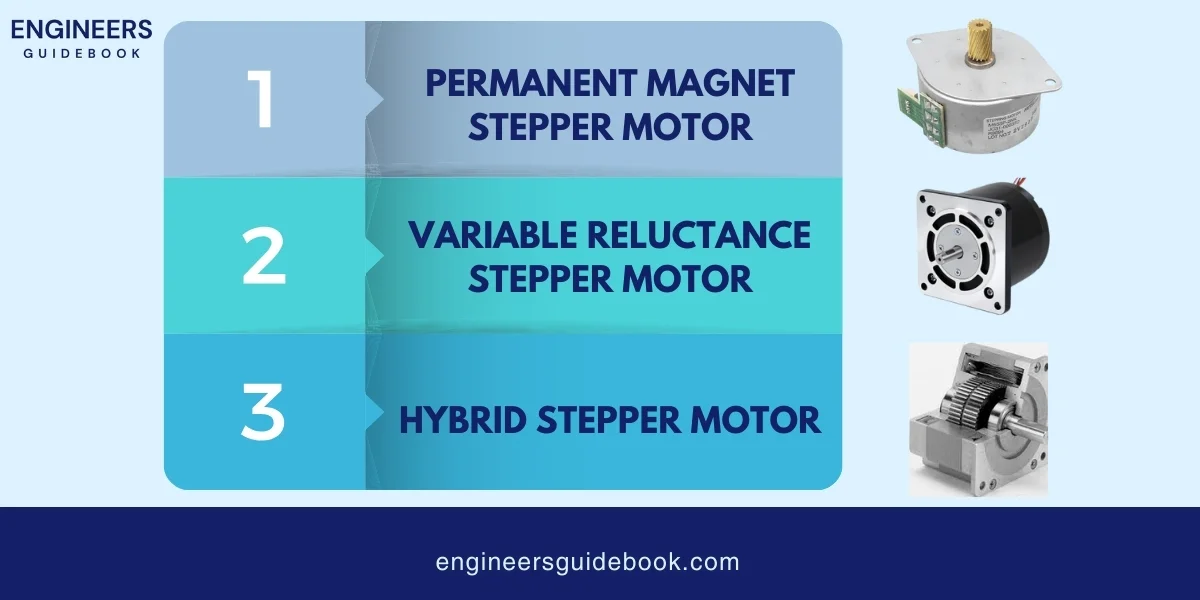
A stepper motor is a type of electric motor that moves in precise steps rather than a continuous motion. It converts electrical pulses into mechanical movement.
Each pulse sent to the motor causes it to move a specific angle, called a step. This makes stepper motors perfect for tasks that need precise control of position and speed.

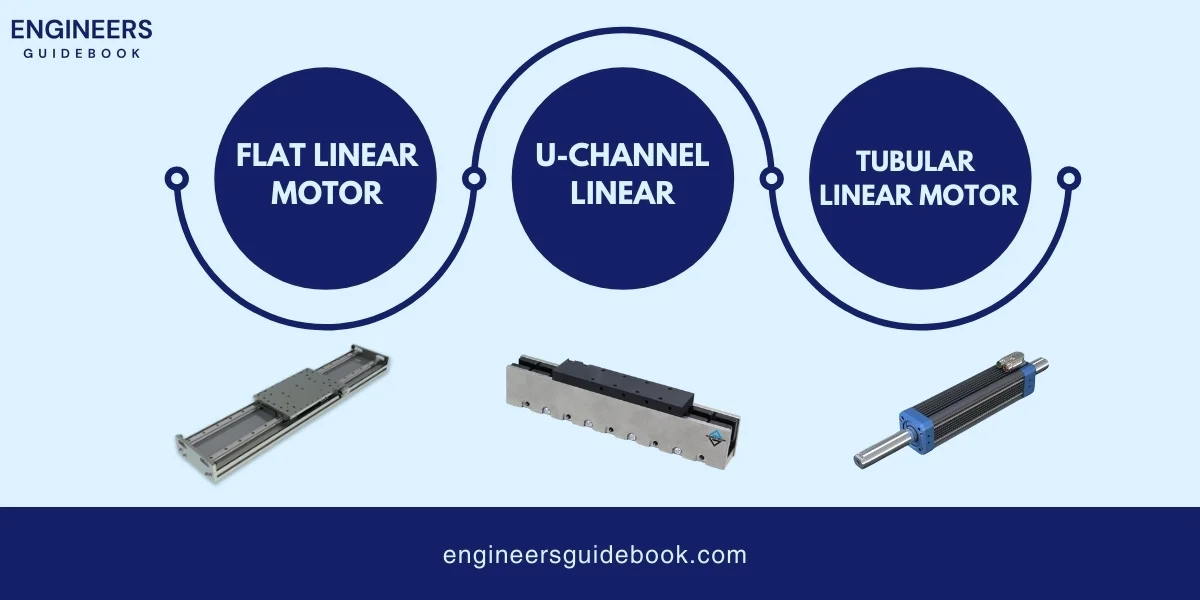
A linear motor is a type of electric motor that produces motion in a straight line instead of a circular motion like most other motors.
It works on the same basic principle as a traditional motor but is unwrapped to provide linear movement. A linear motor has a stationary part called the stator and a moving part called the rotor, or forcer.
When electricity flows through the coils in the stator, it creates a magnetic field that pushes or pulls the forcer along a straight path, creating linear motion.

A torque motor is a special type of motor designed to produce high torque (rotational force) at low speeds, including when the motor is stalled or not moving.
Unlike regular motors, torque motors can provide a steady and strong force without overheating or getting damaged.
They work by using electromagnetic forces to create rotational motion. The stator (stationary part) generates a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor (moving part) to produce torque.

A hysteresis motor is a type of synchronous motor that uses the magnetic properties of a special material in the rotor to produce motion.
The rotor material has a high hysteresis loss, meaning it retains magnetism even after the magnetic field is removed. When the motor is powered on, the stator (stationary part) generates a rotating magnetic field.
This field causes the rotor to magnetize and demagnetize repeatedly, which produces torque and makes the rotor follow the rotating field, thus creating motion.
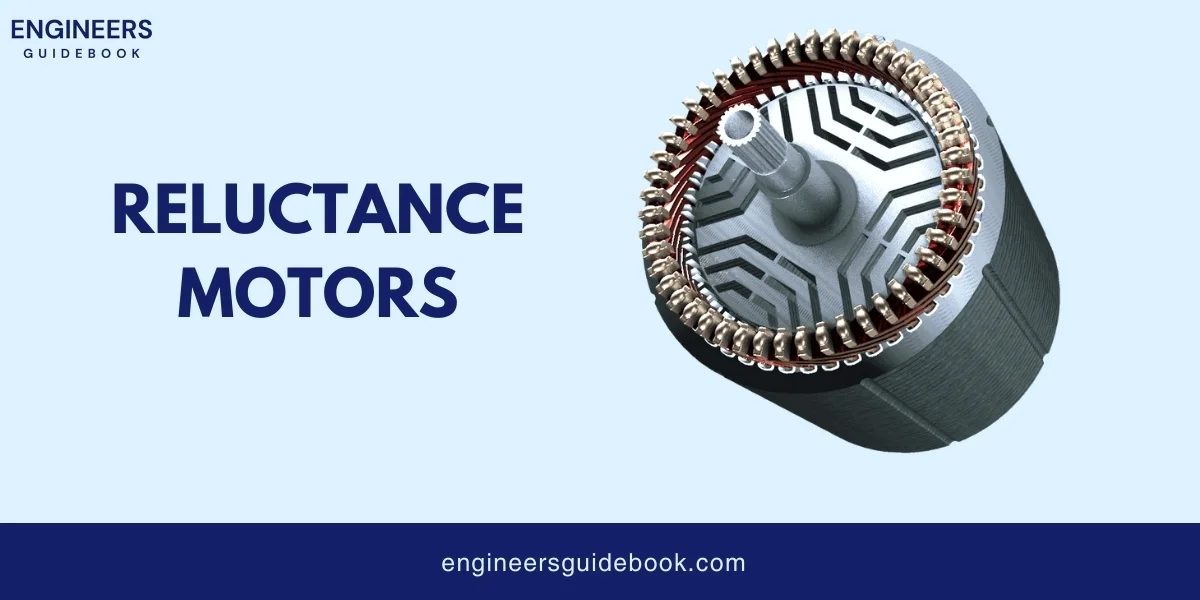
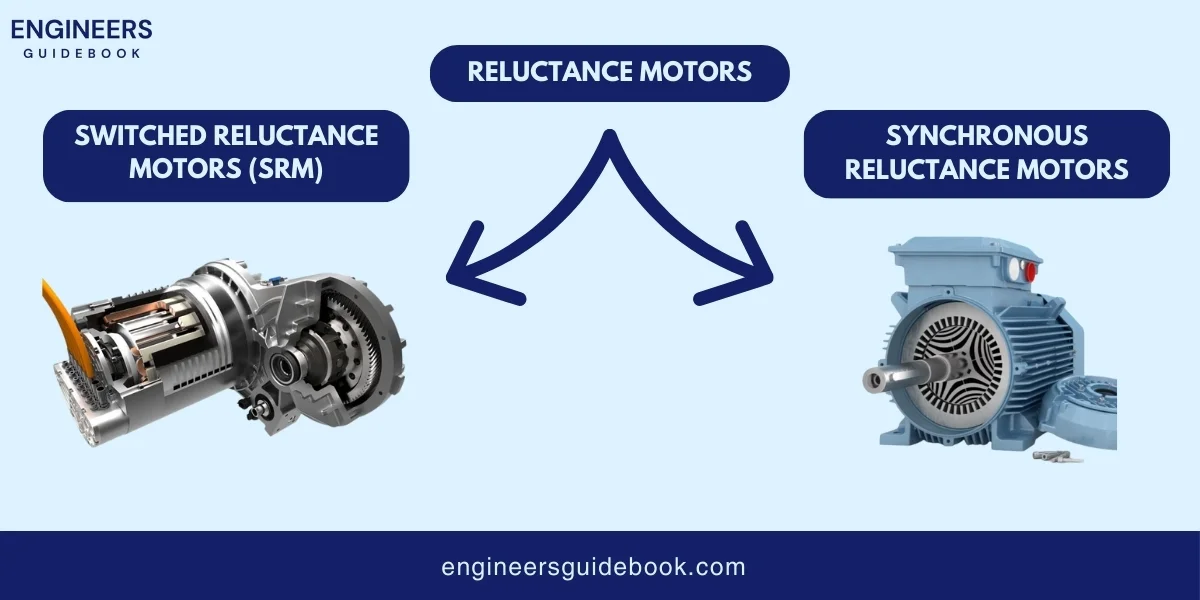
A reluctance motor is a types of AC electric motor that produces motion by creating magnetic reluctance.
Reluctance is a property that resists the flow of magnetic fields. In a reluctance motor, the rotor (the moving part) is designed with areas of different magnetic reluctance.
When the stator (the stationary part) creates a rotating magnetic field, the rotor aligns with the field, reducing reluctance and creating torque. This process causes the rotor to turn, producing motion.
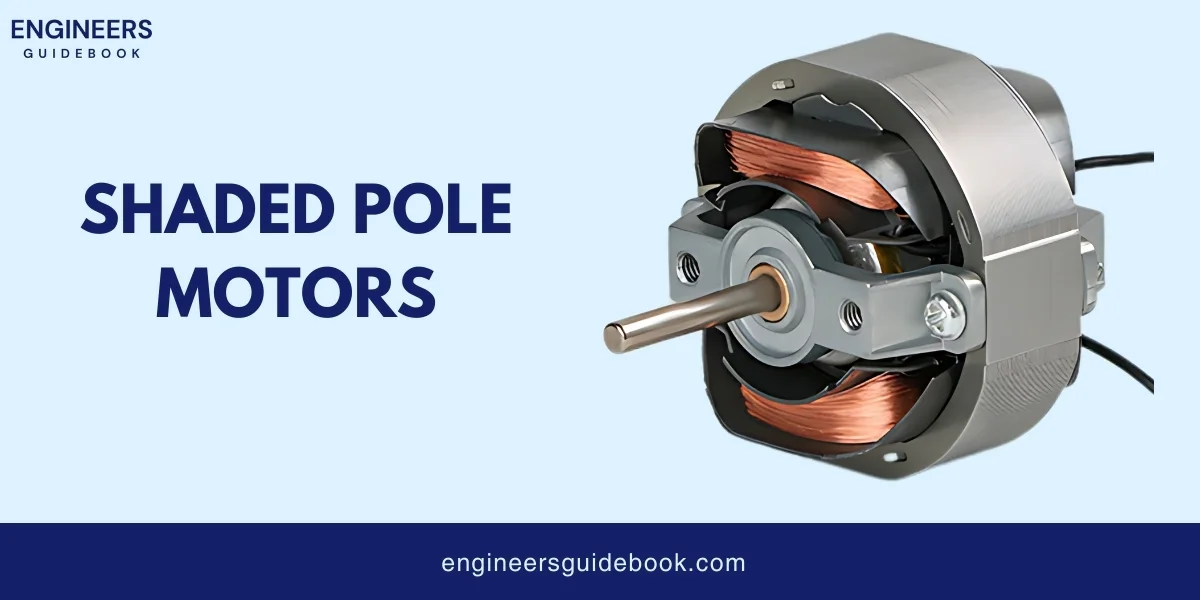
A shaded-pole motor is a simple type of single-phase induction motor. It gets its name from the “shading” coils used in its construction.
The stator (stationary part) has poles, and a portion of each pole is wrapped with a copper ring called a shading coil. When electricity flows through the motor, it creates a magnetic field in the stator.
The shading coils delay the magnetic field in a part of the pole, creating a rotating magnetic field that causes the rotor (the moving part) to turn.

A brushless AC motor is an electric motor that does not use brushes to transfer electricity. Instead, electronic controllers send electric current to the motor’s coils.
The motor has a rotor (the moving part) and a stator (the stationary part). The stator creates a rotating magnetic field that makes the rotor turn. The electronic controller adjusts the current to keep the motor running smoothly and efficiently.

Two-phase motors are electric motors that operate on two-phase AC power. This means they use two alternating currents that are out of phase by 90 degrees. The motor has a stator (the stationary part) and a rotor (the moving part).
The stator has two coils, each powered by one of the two phases. The two currents create a rotating magnetic field that causes the rotor to turn, producing motion.
Understanding the different types of AC motors is essential. Each type of motor has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications.
From the simplicity of shaded-pole motors to the high precision of servo motors, knowing the differences helps in selecting the right motor for the job.
AC motors play a critical role in modern applications, powering everything from household appliances to industrial machinery.
There are 15 main types of AC motors:
These motors vary in design, efficiency, and application suitability, catering to diverse needs in industries, homes, and technology sectors.
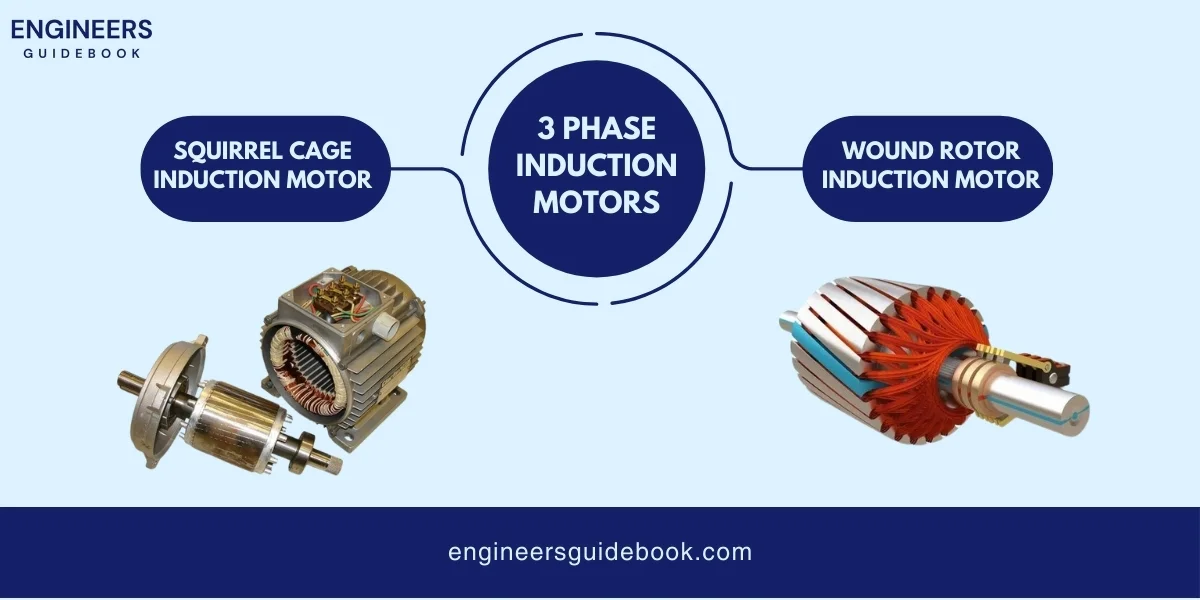
The most popular AC motor is the induction motor, specifically the three-phase induction motor. It is widely used in industrial applications due to its high efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle heavy loads.
Single-phase induction motors are also popular in household appliances and smaller industrial equipment.
AC motors are classified based on their design and operational characteristics.
Types include:
Each type offers unique features suited to different applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery and advanced robotics.
An AC motor is an electric device that changes electrical energy into mechanical energy using AC voltage input.
AC motors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The stator produces a rotating magnetic field that induces a current in the rotor, causing it to spin.
This interaction of the stator and rotor magnetic fields creates a rotational force that makes the motor spin.

A single-phase induction motor is an electrical motor that converts single-phase electrical energy into mechanical energy using magnetic interactions.The motor consists of two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator receives a single-phase AC supply and contains two windings, the main and auxiliary windings.

A three-phase induction motor is a type of electric motor that uses three-phase alternating current (AC) to produce motion.It has two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part and contains coils arranged in three sets, each connected to a different phase of the AC power supply.

A universal motor is a type of electric motor that can run on either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC).This motor has a stator (the stationary part) and a rotor (the rotating part) like other motors. What makes it unique is the way it uses both AC and DC power.

A servo motor is a special type of motor used for precise control of position, speed, and acceleration.It consists of a regular motor coupled with a sensor for position feedback. This motor is controlled by a signal (called a pulse-width modulation signal, or PWM) that tells it how far to move.The servo motor can move to a specific position and hold that position, which makes it very useful in many applications
A stepper motor is a type of electric motor that moves in precise steps rather than a continuous motion. It converts electrical pulses into mechanical movement.
Each pulse sent to the motor causes it to move at a specific angle, called a step. This makes stepper motors perfect for tasks that need precise control of position and speed.

A linear motor is a type of electric motor that produces motion in a straight line instead of a circular motion like most other motors.
It works on the same basic principle as a traditional motor but is unwrapped to provide linear movement. A linear motor has a stationary part called the stator and a moving part called the rotor or forcer.


A torque motor is a special type of motor designed to produce high torque (rotational force) at low speeds, including when the motor is stalled or not moving.
Unlike regular motors, torque motors can provide a steady and strong force without overheating or getting damaged.
A hysteresis motor is a type of synchronous motor that uses the magnetic properties of a special material in the rotor to produce motion.
The rotor material has a high hysteresis loss, meaning it retains magnetism even after the magnetic field is removed. When the motor is powered on, the stator (stationary part) generates a rotating magnetic field.
A hysteresis motor is a type of synchronous motor that uses the magnetic properties of a special material in the rotor to produce motion.
The rotor material has a high hysteresis loss, meaning it retains magnetism even after the magnetic field is removed. When the motor is powered on, the stator (stationary part) generates a rotating magnetic field.


Usman Ahmed, a PhD in Electrical Engineering from Harvard University, is at the forefront of research in smart grid technology. His work on optimizing electrical distribution networks is highly regarded in the academic and professional circles.
Explore the Engineer’s Guidebook! Find the latest engineering tips, industry insights, and creative projects. Get inspired and fuel your passion for engineering.
© 2023-2024 Engineer’s Guidebook. All rights reserved. Explore, Innovate, Engineer.