July 18, 2024 By Muhammad Ali 12 minutes read
Let’s deep dive into the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in engineering. Whether you’re a student just starting or a seasoned professional, this guide will walk you through how AI is revolutionizing the engineering landscape.
From enhancing design processes to predicting maintenance needs, AI is making waves across various engineering fields. So, buckle up as we explore the incredible ways AI is transforming engineering.
Let’s start with the basics. Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is a branch of computer science that aims to create machines capable of intelligent behavior.
This means machines can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and even understanding natural language.
To really grasp how AI works, it’s important to understand its core components. Here are the big three:
Machine Learning (ML): This is a subset of AI where machines are trained to learn from data. Think of it like teaching a dog new tricks. The more data you feed it, the better it gets at performing specific tasks.
Neural Networks: These are algorithms designed to recognize patterns, similar to how the human brain works. They are used in a variety of applications, from image recognition to language processing.
Deep Learning: A more advanced form of neural networks, deep learning involves layers of algorithms that process data in complex ways. This is the technology behind some of the most impressive AI achievements, like self-driving cars and advanced robotics.
AI might seem like a modern marvel, but its roots go back several decades. The concept of AI was first proposed in the 1950s. Since then, it has gone through several phases of development, from simple rule-based systems to the sophisticated machine-learning models we have today.
The recent explosion in AI capabilities can be attributed to advances in computing power, availability of big data, and innovative algorithms.
One of the most significant impacts of AI in engineering is its ability to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Here’s how:
Efficiency: AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data much faster than humans, leading to quicker decision-making and streamlined operations. This efficiency is crucial in fields like manufacturing, where time equals money.
Accuracy: Human errors can be costly in engineering. AI minimizes these errors by providing precise calculations and predictions. For example, in civil engineering, AI can predict the structural integrity of buildings, reducing the risk of failures.
Innovation: AI fosters innovation by offering new ways to solve old problems. Engineers can use AI to simulate and test designs before they are built, leading to more innovative and efficient solutions.
Predictive maintenance involves monitoring the condition of equipment during normal operation to reduce the likelihood of failures. AI plays a crucial role by analyzing large datasets to identify patterns and predict future issues. For example
AI is revolutionizing the design and simulation processes in engineering, making them faster and more accurate. AI-powered tools can generate design alternatives, optimize existing designs, and simulate various scenarios to test performance under different conditions.
AI-powered quality control systems can inspect products and identify defects more accurately than human inspectors. This ensures higher quality products and reduces the risk of defective items reaching customers.
Robotics and automation are fields where AI has made substantial contributions. AI-driven robots can perform complex tasks with high precision and adapt to new tasks quickly, making manufacturing processes more flexible and efficient.
AI optimizes supply chains by predicting demand, managing inventory, and improving logistics. This leads to more efficient operations and reduces the costs associated with overstocking or stockouts.
AI is making a significant impact in civil engineering, from planning and construction to maintenance and management of infrastructure. Let’s explore how AI is transforming this field.
Construction projects are complex, involving numerous variables and stakeholders. AI helps manage these complexities by optimizing schedules, resources, and workflows.
Mechanical engineering has embraced AI to improve processes, product design, and maintenance. Here are some key applications:
AI enhances manufacturing and production processes by improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and ensuring product quality.
Electrical engineering benefits from AI through improved power systems, smart grids, and enhanced electronics. Let’s dive into some specific applications:
AI helps manage and optimize power systems, ensuring efficient and reliable energy distribution.
Chemical engineering has seen AI applications in process optimization, material discovery, and more. Here’s how AI is transforming this field:
AI optimizes chemical processes, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly.
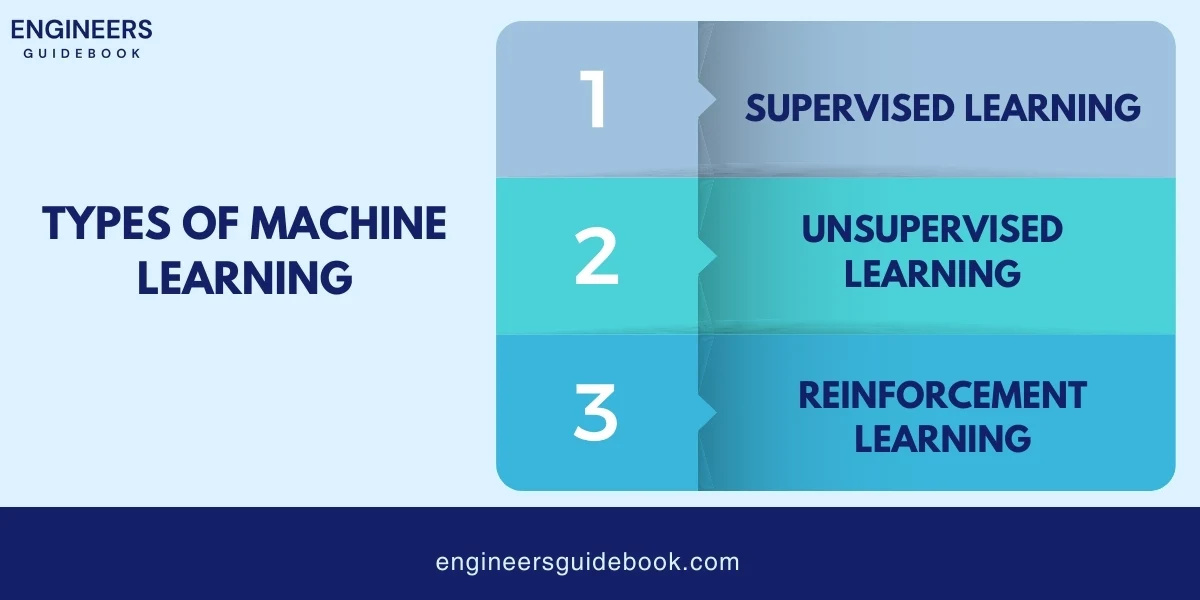
Machine Learning (ML) is at the heart of AI applications in engineering. It enables machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time. Let’s explore the different types of ML algorithms and their applications in engineering.
Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data, where the input and output are known. The model learns to map inputs to outputs and can predict outcomes for new data.
Unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data. The model identifies patterns and relationships in the data without prior knowledge of the output.
Reinforcement learning involves training models to make decisions by rewarding desired behaviors and penalizing undesired ones. This method is particularly useful in dynamic environments.
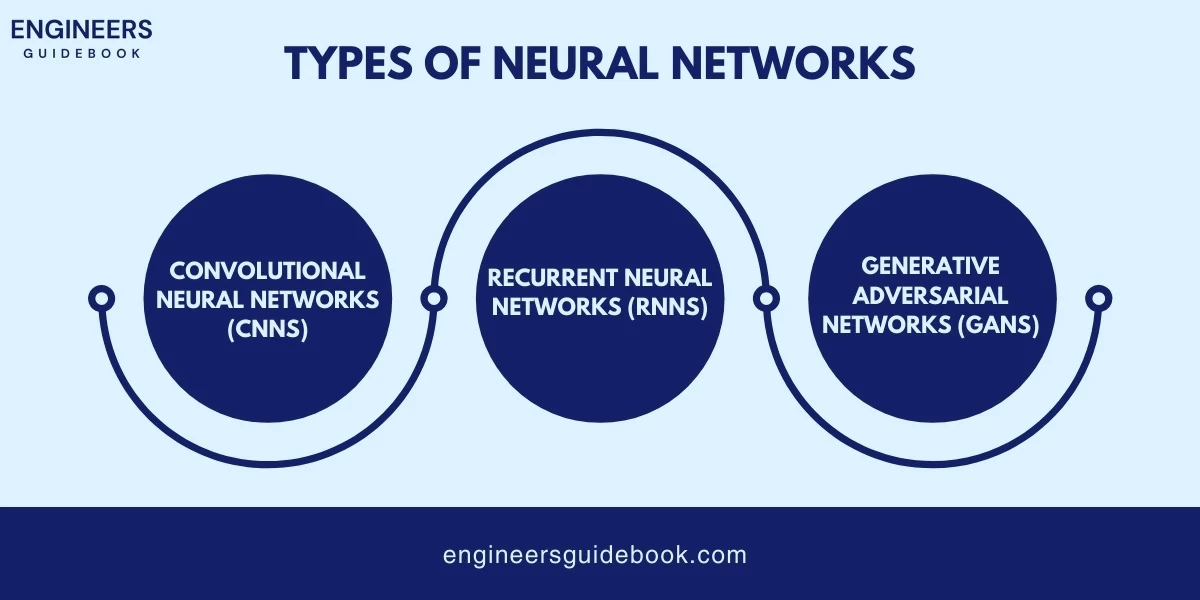
Neural networks are algorithms inspired by the human brain, capable of recognizing patterns and making predictions. Deep learning, a subset of neural networks, involves multiple layers of algorithms that process data in complex ways.
Different types of neural networks are used for various engineering tasks:
Several AI software and platforms are available to engineers, making it easier to implement AI solutions in their projects. Here are some popular tools:
Developed by Google, Tensor Flow is an open-source platform widely used for building and deploying machine learning models. Its flexibility and scalability make it ideal for various engineering applications.
Developed by Facebook, PyTorch is another popular open-source machine-learning library. It is known for its ease of use and dynamic computational graph, making it suitable for research and development.
MATLAB provides a comprehensive environment for numerical computing and is widely used in engineering. Its AI toolbox includes machine learning, deep learning, and reinforcement learning capabilities.
High-quality data is the foundation of effective AI applications. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate models and unreliable predictions.
For AI algorithms to work effectively, they need large amounts of accurate and relevant data. High-quality data ensures that the AI models can learn correctly and make accurate predictions.
The use of AI in engineering raises several ethical and security issues that must be carefully managed.
Company: Delta Air Lines
Challenge: Unplanned maintenance and unexpected equipment failures led to flight delays and cancellations, impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Solution: Delta implemented an AI-based predictive maintenance system. By analyzing data from sensors on aircraft, the AI system predicted when parts would fail, allowing for proactive maintenance.
Outcome: Delta reduced unplanned maintenance by 40%, improved on-time performance, and significantly lowered maintenance costs. The AI system also enhanced safety by ensuring aircraft were always in optimal condition.
Company: General Motors (GM)
Challenge: Designing vehicle components that meet safety, performance, and cost requirements is complex and time-consuming.
Solution: GM used AI-powered design tools to optimize the design of various components. The AI analyzed millions of design options and suggested the best ones based on specified criteria.
Outcome: GM reduced the design cycle time by 30% and achieved better performance and safety standards in their vehicles. The AI-driven approach also led to innovative designs that were not previously considered.
Company: Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E)
Challenge: Managing the distribution of electricity efficiently while integrating renewable energy sources and ensuring reliability.
Solution: PG&E implemented an AI-based smart grid management system. The AI optimized energy distribution, predicted energy demand, and detected faults in the grid.
Outcome: PG&E improved the efficiency of energy distribution, reduced outages, and successfully integrated a higher percentage of renewable energy sources. The AI system also helped in quickly identifying and fixing faults, enhancing overall grid reliability.
Company: Sony
Challenge: Ensuring the highest quality of electronic products while maintaining production speed.
Solution: Sony deployed AI-powered inspection systems in their manufacturing lines. The AI used machine vision to detect defects in real time, identifying issues that were difficult for human inspectors to spot.
Outcome: Sony significantly reduced the defect rate and improved product quality. The AI inspection system also sped up the production process, as it could inspect products much faster than human inspectors.
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets, processes, or systems. They allow engineers to simulate, analyze, and optimize performance in real time.
AI-driven machines and robots are becoming increasingly capable of performing construction tasks autonomously, leading to safer and more efficient construction sites.
AI is set to play a major role in the design process, offering innovative solutions and optimizing designs beyond human capability.
As we have explored throughout this article, Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing the engineering field in numerous ways.
From predictive maintenance and AI-driven design optimization to smart grid management and autonomous construction, AI is making engineering processes more efficient, accurate, and innovative.
The integration of AI in various engineering disciplines, such as civil, mechanical, electrical, and chemical engineering, has shown how powerful AI can be in transforming traditional practices and opening new avenues for advancement.
We have also looked at some of the challenges and considerations that come with implementing AI, such as ensuring data quality, addressing ethical and security concerns, and managing the integration and adoption of AI technologies.
However, these challenges are not insurmountable, and with the right strategies and best practices, the potential benefits of AI in engineering far outweigh the obstacles.

Amber Raza, who earned her PhD in Electrical Engineering from the University of California, Berkeley, is an expert in wireless communication systems. Her innovative research in 5G technology is paving the way for next-generation connectivity.
Explore the Engineer’s Guidebook! Find the latest engineering tips, industry insights, and creative projects. Get inspired and fuel your passion for engineering.
© 2023-2024 Engineer’s Guidebook. All rights reserved. Explore, Innovate, Engineer.
One Response
This is an incredibly insightful and timely article on how AI is truly revolutionizing the engineering landscape! I particularly appreciated how you broke down the tangible benefits of AI, from predictive maintenance and optimizing designs to enhancing simulation capabilities. It’s clear that AI isn’t just a buzzword; it’s becoming an indispensable tool for engineers across various disciplines.
The points about shifting focus to higher-value activities and the need for new skill sets (data literacy, systems thinking) resonate strongly. It really highlights the evolving role of engineers in this AI-driven era.