June 23, 2024 By Muhammad Ali 6 minutes read

In the dynamic world of manufacturing and supply chain management, efficiency and cost reduction are paramount. One strategy that has revolutionized these fields is Just In Time (JIT) inventory management.
Originating from the Toyota Production System, JIT has become a cornerstone of modern production techniques, emphasizing the importance of aligning raw material orders directly with production schedules.
This approach minimizes inventory costs, reduces waste, and enhances overall efficiency, like 5S. This comprehensive guide delves into the principles, benefits, challenges, and modern applications of JIT, providing valuable insights for anyone looking to optimize their production processes.
Just In Time (JIT) is an inventory management strategy that aligns raw-material orders from suppliers directly with production schedules. Its goal is to reduce inventory holding costs and increase efficiency by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process.
The idea of JIT started a long time ago in Japan. It became really famous because of a car company you might have heard of—Toyota! In the 1970s, Toyota wanted to make their car production super efficient.
They figured out that having too many car parts lying around was a waste of space and money. So, they started ordering parts only when they were needed for making cars. This smart idea is what we now call Just In Time (JIT).
Since then, the JIT method has spread all over the world. Companies in different industries, not just car makers, use JIT to save money and space.
It has evolved with new technologies and ideas, but the main goal remains the same: getting the right materials at the right time.
The main goals of JIT are pretty straightforward:
There are several key components that help companies implement JIT effectively. Let’s break them down one by one.
Lean manufacturing is like JIT’s best friend. They work together to make production super efficient. Lean manufacturing focuses on getting rid of waste.
Waste can be anything from extra materials to too much time spent on one task. By using lean manufacturing, companies can make sure they’re only doing what’s necessary and nothing extra. This makes the whole process smoother and faster.
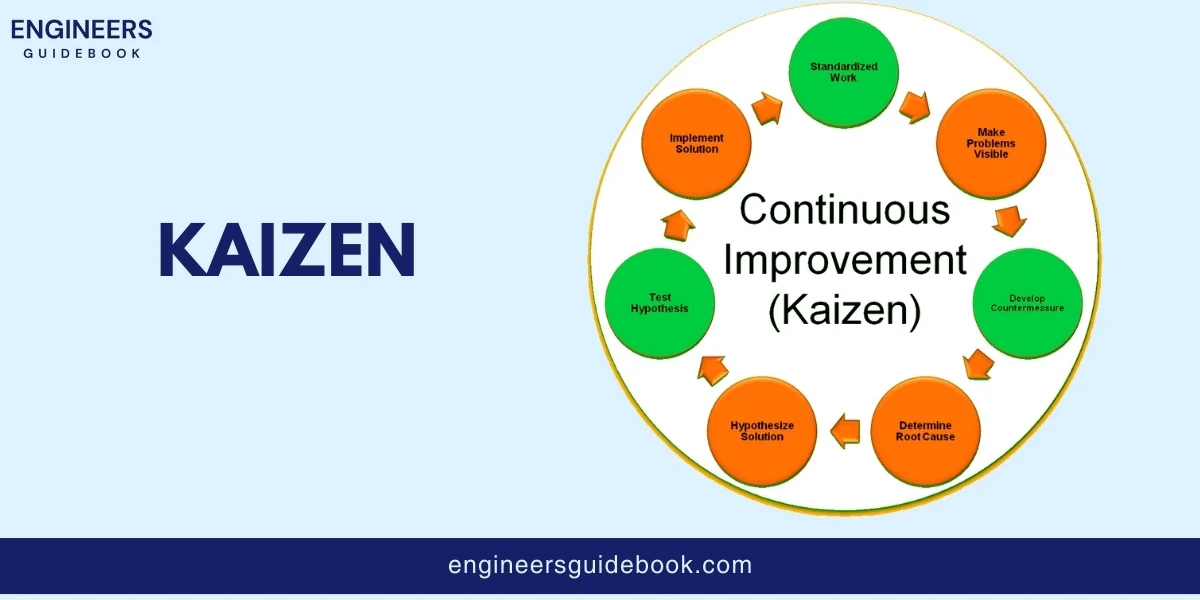
Kaizen is a Japanese word that means “change for the better.” It’s all about making small improvements every day. In JIT, continuous improvement means always looking for ways to make the production process better.
It could be something simple like reorganizing tools to save time or finding a new supplier who delivers faster.
The idea is that lots of small changes can add up to big improvements.
Imagine you’re at a buffet. Instead of filling your plate with everything at once, you take food as needed. That’s what the pull system is like in JIT.
It means that production is based on customer demand. Companies only make or order what’s needed when it’s needed.
This helps them avoid having too much inventory and reduces waste.
Kanban is a visual tool that helps manage the workflow in JIT. Think of it as a big board with cards on it. Each card represents a task or an item that needs to be done.
As tasks move through the production process, the cards move on the board. This helps everyone see what’s happening and what needs to be done next.
It’s a simple but powerful way to keep everything organized and on track.
There are several benefits that make JIT a popular choice for many businesses.
One of the biggest benefits of JIT is reducing inventory. Remember the candy shop example? By only having the candy you need when you need it, you don’t have to worry about it going stale.
In the same way, companies using JIT only order materials when they need them.
This means they don’t have to store a lot of extra stuff, which saves space and money.
With JIT, everything is streamlined. There’s no waiting around for materials because they arrive just in time for production.
This makes the whole process faster and more efficient. Workers can focus on what they need to do without being slowed down by missing parts or too much clutter.
Since JIT focuses on getting things done right when they’re needed, it often leads to better quality products.
There’s less chance of materials getting damaged while sitting in storage.
Plus, continuous improvement means that any quality issues are quickly identified and fixed.
By reducing inventory and increasing efficiency, companies can save a lot of money.
They don’t have to spend as much on storage or waste materials.
Plus, a more efficient process means lower labour costs because workers can get more done in less time.
Let’s explore some of the common issues companies might face when trying to implement JIT.
Implementing JIT isn’t always easy. It requires careful planning and a lot of effort. Companies need to make sure all parts of their production process are aligned perfectly.
This can be tough, especially if they have been using a different system for a long time.
Changing the way things are done can be hard for everyone involved, from management to workers on the factory floor.
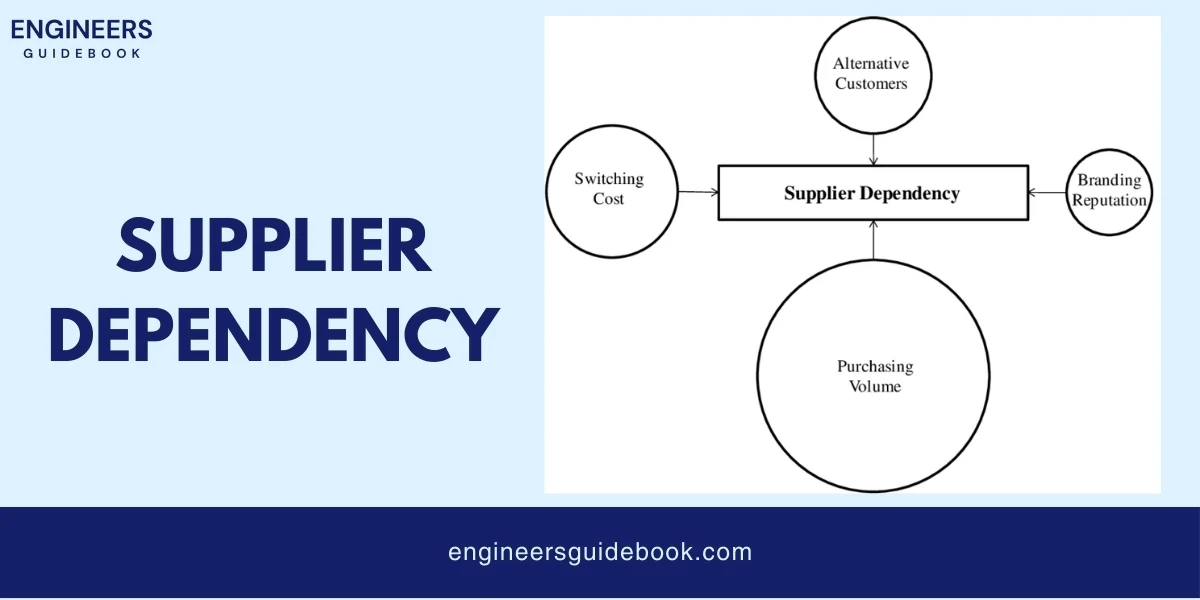
One of the biggest risks with JIT is relying heavily on suppliers. Since companies only order materials when they need them, any delay from a supplier can cause big problems.
Imagine if the candy shop ordered chocolate chips, but the delivery was late. They wouldn’t be able to make cookies on time!
In the same way, any disruption in the supply chain can stop production, leading to delays and unhappy customers.
With JIT, companies are very dependent on their suppliers. They need to have reliable suppliers who can deliver high-quality materials on time.
If a supplier goes out of business or faces issues, it can create a major problem.
Companies need to have good relationships with their suppliers and maybe even backup suppliers to avoid any interruptions.
JIT can sometimes be inflexible. Because companies only order what they need when they need it, they might not be able to respond to sudden changes in demand quickly.
For example, if the candy shop suddenly gets a big order for cookies, they might not have enough ingredients on hand to meet the demand.
This lack of flexibility can be a problem, especially in industries where demand can change rapidly.
Implementing JIT requires employees to be well-trained and understand the new processes.
Workers need to be on board with the changes and know how to handle the new system. This can involve a lot of training and sometimes even changing the way employees think about their work.
It’s not just about learning new skills but also about adopting a new mindset focused on efficiency and continuous improvement.

Let’s go through the steps and key components needed for a successful JIT implementation.
Before jumping into JIT, companies need to do some serious planning. This involves analyzing their current processes to understand where improvements can be made.
Companies should map out their production steps to see where waste occurs and identify areas that can be streamlined.
It’s crucial to set clear goals and timelines for the JIT implementation to keep everyone on track.
Employees play a vital role in making JIT work. They need to understand the new processes and their importance.
Training programs should be set up to educate workers about JIT principles and how to apply them in their daily tasks.
It’s not just about learning new procedures but also about adopting a new way of thinking focused on efficiency and continuous improvement.
Process mapping involves creating a visual representation of the production process.
This helps identify steps that don’t add value and can be eliminated. By mapping out the entire workflow, companies can spot bottlenecks and areas where materials get stuck.
This step is essential for streamlining operations and ensuring a smooth transition to JIT.
Modern technology plays a big part in successful JIT implementation.
Tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and automation can help manage inventory and production schedules efficiently.
ERP systems integrate all aspects of the business, from inventory to finance, making it easier to coordinate JIT processes.
Automation can speed up production and reduce errors, ensuring materials are available when needed.
These case studies will show you how companies from various fields have implemented JIT and the benefits they’ve gained.
Toyota is the company that made JIT famous. In their factories, they only keep a small amount of parts on hand and order more as they need them.
This helps them save space and money. They also use a pull system, meaning they produce cars based on customer orders rather than keeping a large inventory.
This approach has made Toyota one of the most efficient car manufacturers in the world.
Dell, a leading computer manufacturer, uses JIT to build custom computers based on individual orders. When a customer orders a computer, Dell only then assembles it using parts that arrive just in time.
This method allows Dell to offer a wide variety of customizations without needing to keep a large inventory of parts.
It also helps them reduce costs and respond quickly to changes in customer demand.
Boeing, the aerospace giant, uses JIT to streamline its production process. Building aeroplanes requires thousands of different parts, and Boeing only orders these parts as they are needed for assembly.
This method reduces the amount of inventory they need to store and lowers costs.
It also helps them maintain flexibility in their production process, allowing them to adjust quickly to new orders or changes in demand.
Some hospitals use JIT to manage their medical supplies. Instead of stocking large amounts of medical equipment and medications, they order them as needed.
This approach ensures that supplies are always fresh and up-to-date. It also helps hospitals save on storage space and costs.
In today’s world, modern technologies are making Just In Time (JIT) even more efficient.
In JIT, IoT devices can track inventory levels in real-time and automatically order new materials when supplies run low.
For example, smart sensors in a warehouse can monitor stock levels and send alerts when it’s time to reorder.
This ensures that materials arrive just in time for production, reducing the risk of running out of stock.
In JIT, data analytics can predict customer demand and help companies plan their production schedules more accurately.
By analyzing sales data, companies can forecast how much product they will need and when they will need it.
This helps them order the right amount of materials at the right time, reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
AI can analyze data to optimize production schedules and make real-time adjustments.
For example, if there is a sudden increase in demand for a product, AI can adjust the production schedule to meet this demand.
Automation, on the other hand, can handle repetitive tasks like moving materials around a warehouse.
This speeds up the production process and reduces the chance of human error.
Just In Time (JIT) is one of several inventory management systems. Let’s compare JIT with two other common systems:
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a system used to plan the materials needed for production. Here’s how it differs from JIT:
Despite these differences, MRP and JIT can work together. For example, MRP can be used for long-term planning and forecasting, while JIT can handle the day-to-day inventory management.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive system that integrates all aspects of a business, including inventory management, finance, human resources, and more. Here’s how it compares to JIT:
Combining ERP with JIT can enhance overall business efficiency. ERP can provide the data and integration needed for effective JIT implementation, ensuring that inventory management is aligned with other business processes.
Let’s look at some emerging trends and innovations that are shaping the future of JIT and how it contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices.
Smart Manufacturing: The rise of smart manufacturing, which uses advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and machine learning, is making JIT more efficient.
These technologies help companies predict demand more accurately, manage inventory in real time, and automate processes.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance JIT by providing secure, transparent tracking of materials throughout the supply chain.
This ensures that materials are sourced responsibly and arrive on time.
3D Printing: Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing allows companies to produce parts on demand.
This aligns perfectly with JIT principles, as it reduces the need for large inventories and speeds up the production process.
JIT is naturally aligned with sustainable manufacturing practices. Here’s how it contributes:
Just In Time (JIT) is a powerful inventory management strategy that can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce costs for companies. By understanding its historical background, key components, benefits, challenges, and the role of modern technologies, businesses can successfully implement JIT in their operations.
While JIT offers numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and challenges, such as dependency on suppliers and flexibility issues. Combining JIT with other inventory management systems like MRP and ERP, and leveraging emerging technologies, can further optimize the production process.
By continuously improving and adapting JIT practices, companies can achieve sustainable and efficient manufacturing processes, ensuring they stay competitive in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Just In Time (JIT) is an inventory management strategy that aligns raw-material orders from suppliers directly with production schedules. This system aims to reduce inventory holding costs and increase efficiency by receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process
JIT is crucial because it minimizes inventory costs, reduces waste, and increases efficiency. By having materials arrive just in time for production, businesses avoid the costs associated with storing excess inventory and can respond more quickly to changes in demand
The primary benefits of JIT include:
Implementing JIT can be challenging due to:
IT requires strong, reliable relationships with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of materials. Any delays or disruptions in the supply chain can halt production, making it critical to have dependable suppliers and sometimes backup options
JIT is particularly beneficial for manufacturing businesses with high-volume inventory turnover, such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries. Retailers and healthcare providers also benefit from JIT by reducing inventory costs and improving efficiency
JIT contributes to sustainability by reducing waste and ensuring efficient use of resources. By ordering only what is needed, companies minimize excess production and inventory, which lowers their environmental footprint
The main risks include:
JIT improves efficiency by ensuring that materials are available exactly when needed, reducing downtime, and streamlining the production process. This leads to faster production cycles and less wasted time and resources

Muhammad Ali holds a PhD in Mechanical Engineering from MIT and is currently conducting groundbreaking research on sustainable energy systems. His innovative work in renewable energy integration has earned him numerous accolades in the engineering community.
Explore the Engineer’s Guidebook! Find the latest engineering tips, industry insights, and creative projects. Get inspired and fuel your passion for engineering.
© 2023-2024 Engineer’s Guidebook. All rights reserved. Explore, Innovate, Engineer.