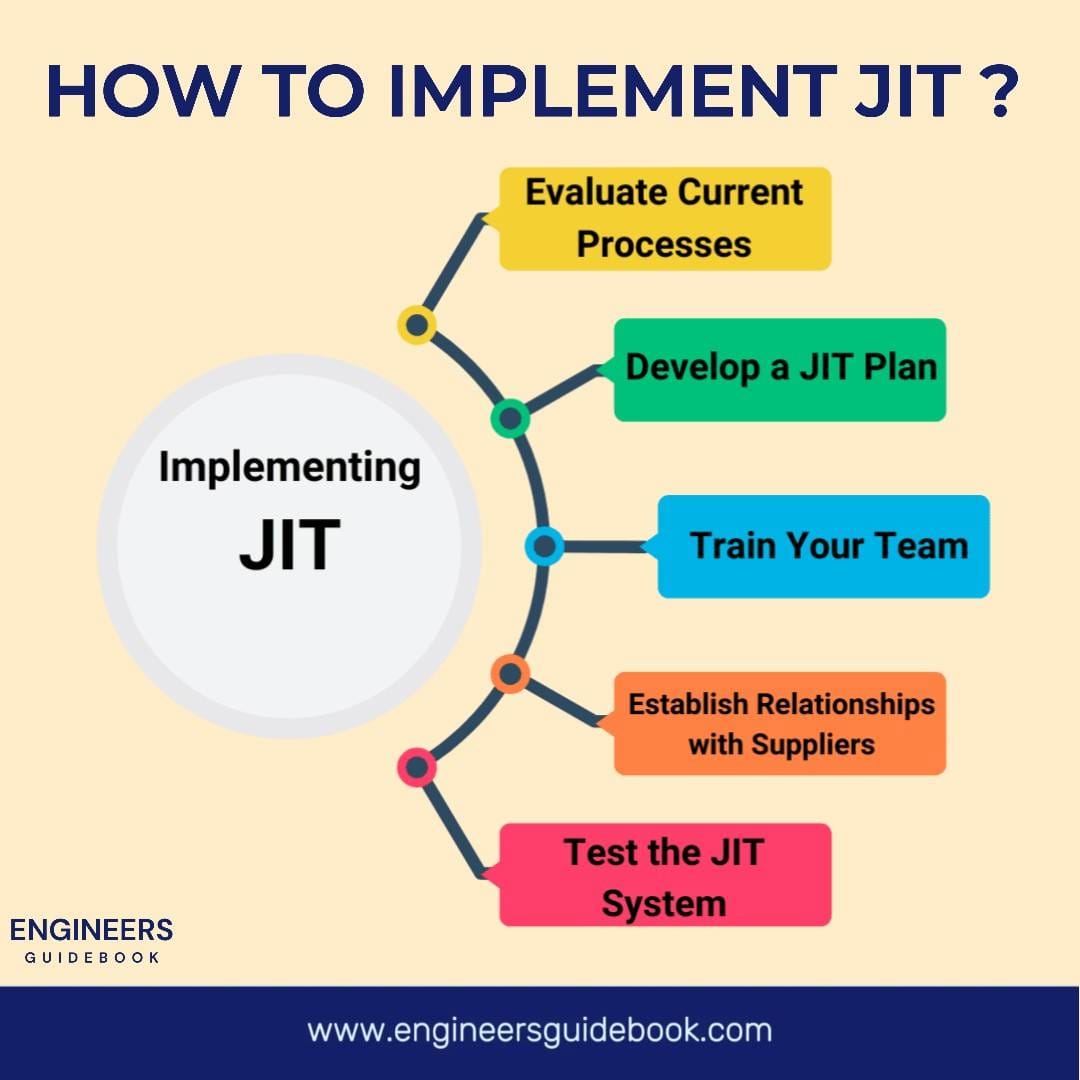
1. Understanding Just-In-Time (JIT) and Its Core Principles
1.1 The Origins and Evolution of JIT
The Just-In-Time (JIT) methodology traces its roots to post-war Japan, where resource constraints necessitated innovative manufacturing solutions. Toyota, under the leadership of Taiichi Ohno, pioneered this approach to streamline production, minimize waste, and enhance efficiency. Inspired by American supermarkets’ inventory replenishment strategies, Toyota developed JIT to ensure materials arrived precisely when needed, eliminating excess stock and associated costs. Over time, JIT evolved into a global best practice, influencing industries beyond automotive manufacturing, including healthcare, retail, and logistics. In this guide, we will discuss in detail how you can implement JIT in your business.
1.2 Key Principles of JIT
At its core, JIT revolves around lean operations, striving to eradicate inefficiencies in production and supply chains. The primary principles include:
- Inventory Minimization: Holding only essential stock to reduce carrying costs.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Incremental enhancements to refine processes.
- Demand-Driven Production: Aligning manufacturing schedules with customer demand.
- Supplier Integration: Establishing strong, reliable supplier partnerships.
- Elimination of Waste (Muda): Identifying and eliminating non-value-adding activities. By adhering to these principles, businesses can optimize workflows, minimize costs, and enhance responsiveness to market fluctuations.
1.3 How JIT Transforms Business Operations
The adoption of JIT can lead to profound operational transformations. It fosters enhanced coordination between procurement, production, and distribution, ensuring seamless workflows. Businesses implementing JIT often experience reduced lead times, improved product quality, and greater agility in responding to consumer demand. Additionally, JIT promotes lean thinking across all levels of an organization, fostering a culture of efficiency and continuous improvement.
1.4 Common Misconceptions About JIT
Despite its proven benefits, JIT is sometimes misunderstood. A prevalent myth is that JIT eliminates inventory entirely, whereas it merely optimizes stock levels to balance demand and supply efficiently. Another misconception is that JIT is only suitable for large enterprises; in reality, businesses of all sizes can adapt JIT principles to enhance operational efficiency.
Additionally, some assume JIT is incompatible with unpredictable demand; however, integrating JIT with advanced forecasting techniques can mitigate risks associated with fluctuating consumer preferences.
Also Read:
Just In Time (JIT): A Comprehensive Guide for Engineers
2. Assessing Your Business Readiness for JIT Implementation
2.1 Identifying Current Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies
Before implementing JIT, businesses must conduct a thorough assessment of existing operational inefficiencies. Identifying common bottlenecks. such as production delays, overstocked inventory, or supplier inconsistencies provide a clear roadmap for improvement. Analyzing workflow disruptions and material flow constraints ensures targeted interventions that align with JIT objectives.

2.2 Analyzing Inventory Management Practices
A critical component of JIT readiness is evaluating current inventory management strategies. Businesses must assess stock levels, turnover rates, and demand variability. High levels of obsolete or slow-moving inventory indicate inefficiencies that JIT can rectify. Implementing accurate demand forecasting and real-time tracking systems can enhance inventory control, reducing carrying costs and minimizing stockouts.
2.3 Evaluating Supplier Relationships and Supply Chain Stability
JIT’s success heavily depends on reliable suppliers who can deliver materials on demand. Businesses must evaluate supplier capabilities, response times, and logistical efficiencies. Establishing strategic partnerships with vendors who can provide just-in-time deliveries ensures seamless production continuity. Additionally, diversifying supplier networks can mitigate risks associated with potential disruptions.
2.4 Assessing Workforce Readiness and Skills
JIT implementation necessitates a workforce that understands lean methodologies and embraces continuous improvement. Assessing employee readiness involves evaluating their adaptability, problem-solving skills, and familiarity with lean practices. Training programs on waste reduction, standardized work procedures, and process optimization can enhance workforce efficiency, ensuring smooth JIT adoption.

2.5 Determining Technological Capabilities for JIT
Technology plays a pivotal role in JIT execution. Businesses must evaluate their existing IT infrastructure, automation capabilities, and data analytics tools. Implementing real-time tracking systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, and predictive analytics can facilitate seamless coordination between production schedules and inventory management, reinforcing JIT principles.
3. Designing a JIT Implementation Strategy
3.1 Setting Clear Objectives and Performance Metrics
Defining measurable objectives is crucial for successful JIT deployment. Businesses should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover rates, order fulfillment accuracy, and production cycle times. Clear benchmarks enable organizations to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and refine JIT strategies accordingly.

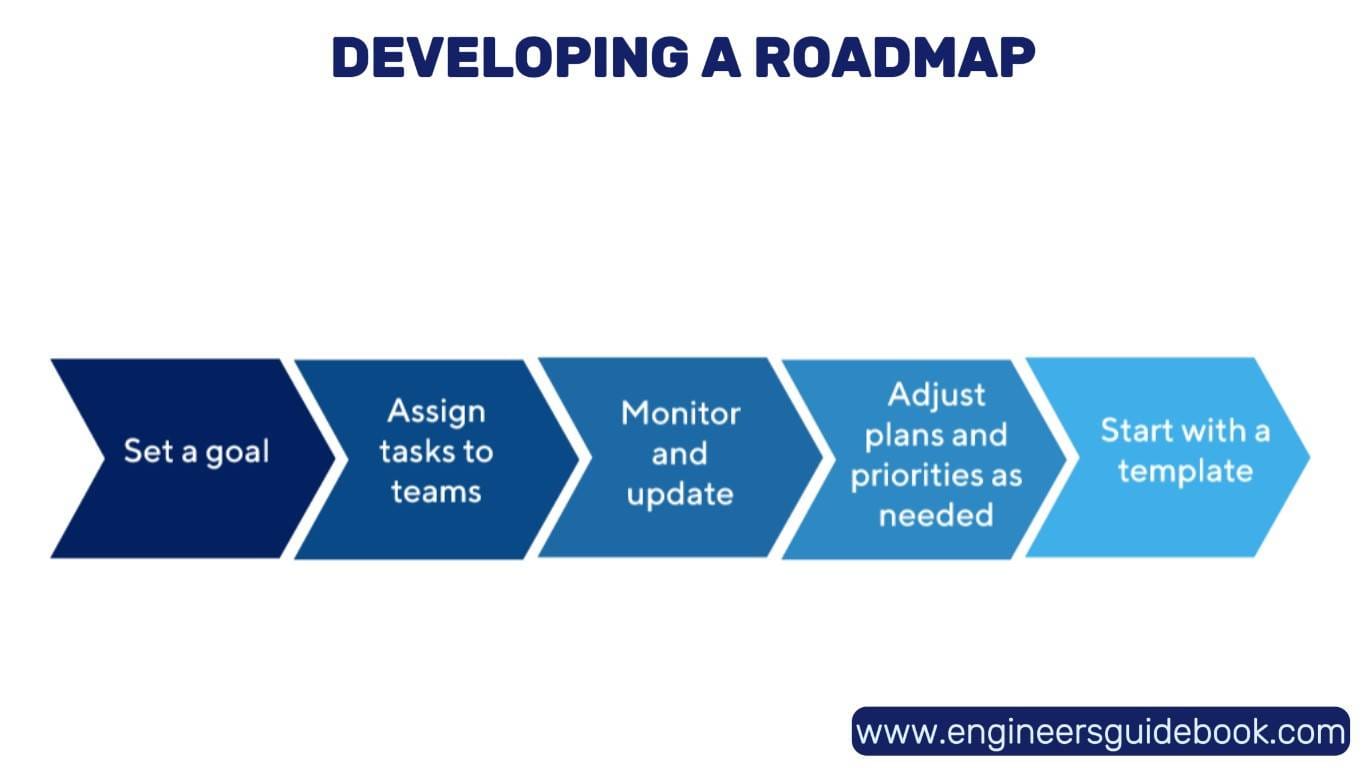
3.2 Developing a Roadmap for Gradual Implementation
Rather than an abrupt overhaul, businesses should adopt a phased JIT implementation approach. Transitioning incrementally—starting with pilot programs in select departments—allows organizations to refine processes before scaling up. This step-by-step strategy minimizes operational disruptions and ensures smoother integration across all business functions.
3.3 Engaging Key Stakeholders: Employees, Suppliers, and Customers
Stakeholder engagement is paramount to JIT success. Employees need thorough training to understand JIT principles and their role in process optimization. Suppliers must align with JIT requirements, ensuring timely material deliveries. Additionally, businesses should manage customer expectations by communicating how JIT can enhance product availability and lead times.
3.4 Building a Cross-Functional JIT Implementation Team
A dedicated implementation team comprising representatives from procurement, production, logistics, and IT can drive JIT initiatives effectively. Cross-functional collaboration fosters holistic decision-making, ensuring alignment between operational departments. Regular meetings, progress tracking, and feedback loops facilitate continuous improvement in JIT execution.

4. Streamlining Inventory Management with JIT
4.1 Eliminating Excess Stock Without Disrupting Operations
JIT emphasizes maintaining lean inventory levels while ensuring uninterrupted production. Businesses should analyze historical demand patterns and eliminate unnecessary stockpiles. Implementing safety stock buffers for critical components mitigates supply chain risks, ensuring smooth operations without excessive inventory.
4.2 Adopting a Demand-Driven Approach to Procurement
Shifting from traditional bulk purchasing to a demand-driven procurement strategy optimizes inventory costs. Businesses should align purchasing schedules with real-time demand fluctuations, leveraging just-in-time ordering systems to minimize holding costs. Establishing close communication channels with suppliers enhances responsiveness to production needs.
4.3 Using Lean Warehousing to Optimize Storage Space
JIT-driven lean warehousing principles reduce unnecessary storage costs and improve space utilization. Implementing organized shelving systems, barcode scanning, and FIFO (First-In-First-Out) inventory rotation ensures efficient warehouse management. Minimizing stock obsolescence and streamlining retrieval processes enhance overall warehouse efficiency.
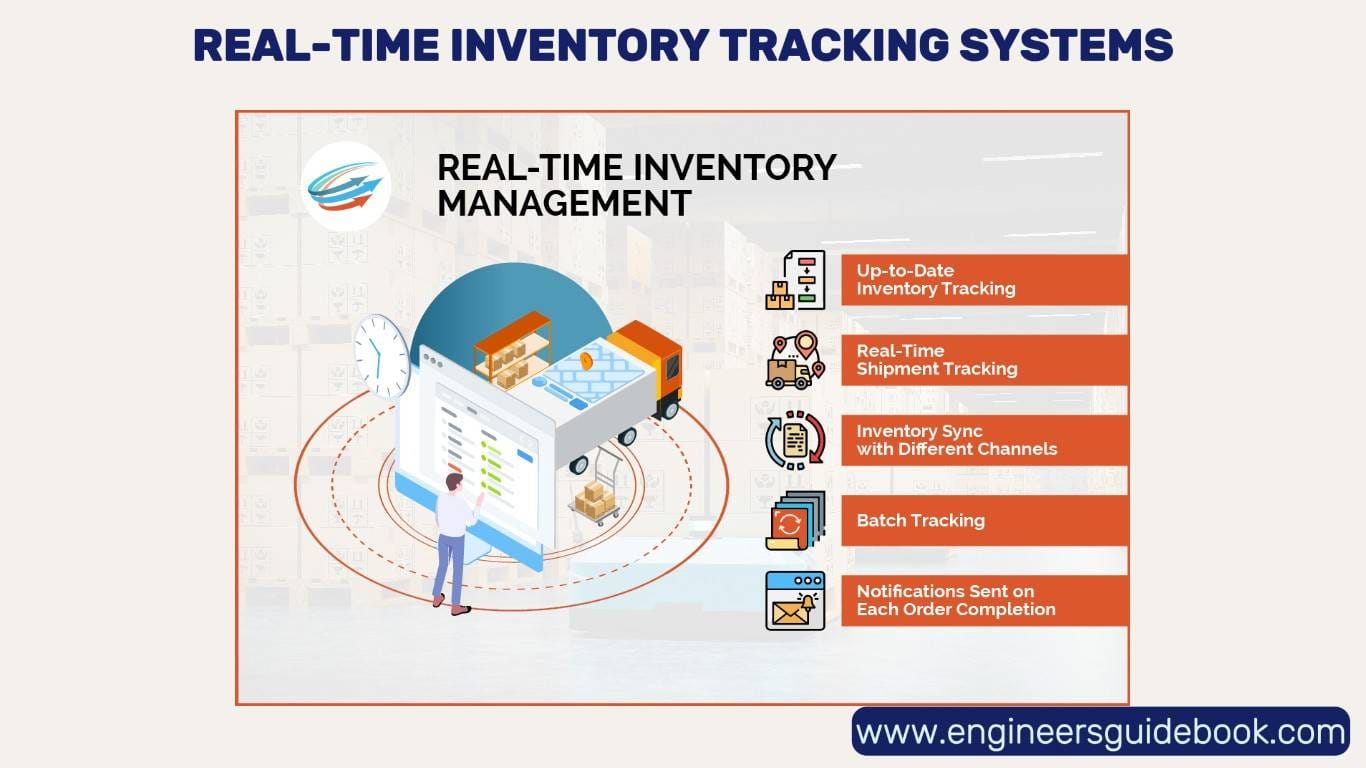
4.4 Implementing Real-Time Inventory Tracking Systems
Real-time inventory tracking solutions enable businesses to maintain optimal stock levels while preventing shortages. Utilizing RFID technology, IoT-enabled sensors, and cloud-based ERP systems ensures accurate stock visibility across supply chains. Automated alerts for low stock levels facilitate timely replenishment, preventing disruptions in production workflows.
5. Optimizing Production Processes for JIT
5.1 Reducing Setup Times and Enhancing Workflow Efficiency
Minimizing setup times is essential for JIT success. Implementing Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED) techniques can drastically cut down machine changeover durations, ensuring smoother transitions between production runs. Analyzing workflow inefficiencies, eliminating redundant steps, and streamlining material flow contribute to leaner operations. Businesses should also implement visual management tools such as kanban boards to optimize scheduling and workflow coordination.
5.2 Establishing Standardized Work Procedures
Standardized work ensures consistency and efficiency in production processes. Developing detailed work instructions, process maps, and standard operating procedures (SOPs) eliminates variability in output. Encouraging frontline workers to participate in standardization efforts fosters engagement and ensures practical, executable processes. Implementing error-proofing techniques, such as Poka-Yoke, further enhances reliability and reduces production defects.
5.3 Implementing Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) in Production
Kaizen, or continuous improvement, is a fundamental principle of JIT. Encouraging employees at all levels to identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements fosters a culture of innovation. Implementing small, incremental changes leads to long-term efficiency gains. Regular Kaizen events, such as value stream mapping and Gemba walks, help businesses identify bottlenecks and refine production workflows. Creating cross-functional teams to address systemic issues ensures sustainable progress.

5.4 Integrating Automation and Smart Manufacturing Technologies
Technology plays a pivotal role in optimizing JIT production. Automating repetitive tasks through robotic process automation (RPA) reduces cycle times and minimizes errors. Smart manufacturing technologies, such as AI-driven quality control and digital twins, enable real-time process optimization. Implementing industrial IoT (IIoT) sensors on machinery facilitates predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and ensuring seamless production continuity.
6. Strengthening Supplier Relationships for Seamless JIT Operations
6.1 Selecting Reliable Suppliers with Quick Response Capabilities
The success of JIT hinges on dependable suppliers capable of delivering materials just in time. Businesses must evaluate suppliers based on responsiveness, lead time reliability, and quality consistency. Developing criteria for supplier selection—such as adherence to lean principles, financial stability, and logistical efficiency—ensures uninterrupted production flow. Supplier scorecards can help track performance and identify potential areas for improvement.
6.2 Developing Long-Term Strategic Partnerships
Building long-term relationships with suppliers fosters mutual trust and collaboration. Engaging suppliers in continuous improvement initiatives strengthens supply chain resilience. Implementing joint development programs, knowledge-sharing workshops, and regular performance reviews enhances coordination. Collaborative forecasting and demand-sharing mechanisms enable suppliers to align their production schedules with business needs.
6.3 Implementing Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) streamlines stock replenishment and reduces administrative burden. Under VMI, suppliers monitor inventory levels and restock materials based on real-time consumption data. This approach eliminates stockouts and prevents overstocking, improving overall efficiency. Implementing electronic data interchange (EDI) or cloud-based inventory management systems enhances visibility and coordination between suppliers and manufacturers.
6.4 Negotiating Flexible and Responsive Supply Contracts
Traditional rigid contracts may hinder JIT adaptability. Businesses should negotiate flexible agreements that accommodate demand fluctuations. Implementing rolling forecasts, tiered pricing structures, and just-in-time delivery clauses ensures suppliers can adjust to changing requirements. Contracts should also include contingency plans to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
7. Improving Workforce Efficiency and Engagement
7.1 Training Employees on JIT Principles and Best Practices
A well-trained workforce is essential for effective JIT implementation. Employees should receive comprehensive training on lean manufacturing principles, waste reduction techniques, and real-time problem-solving strategies. Hands-on workshops, simulation exercises, and on-the-job training sessions reinforce theoretical knowledge with practical applications.
7.2 Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
JIT thrives in an environment that encourages proactive problem-solving. Leadership should cultivate a mindset of continuous improvement by recognizing and rewarding innovative contributions. Implementing structured problem-solving methodologies, such as the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, empowers employees to identify inefficiencies and implement corrective actions. Open communication channels and feedback loops facilitate sustained engagement.
7.3 Encouraging Cross-Training to Enhance Workforce Flexibility
Cross-training employees across multiple roles enhances adaptability in a JIT environment. Workforce flexibility ensures production continuity during unexpected absences or demand surges. Implementing job rotation programs and multi-skill training sessions diversifies skill sets, fostering resilience and reducing dependency on specialized personnel.
7.4 Establishing Performance Metrics and Incentives for JIT Success
Defining clear performance indicators ensures alignment with JIT objectives. Metrics such as takt time, overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), and defect rates provide actionable insights into operational efficiency. Implementing incentive programs that reward efficiency gains, cost reductions, and process optimizations motivates employees to sustain high performance levels.
8. Leveraging Technology for JIT Implementation
8.1 Using Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) for JIT Coordination
ERP systems serve as the backbone of JIT operations, enabling real-time data integration across procurement, production, and distribution. Advanced ERP platforms facilitate demand forecasting, inventory tracking, and supplier collaboration. Customizing ERP modules to align with JIT principles enhances operational synchronization and decision-making accuracy.
8.2 Implementing Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for JIT success. Leveraging predictive analytics powered by artificial intelligence (AI) enhances forecasting accuracy by analyzing historical data, market trends, and external variables. Machine learning algorithms can identify demand patterns, enabling businesses to adjust procurement schedules dynamically. Implementing demand-driven replenishment strategies minimizes excess inventory while ensuring product availability.
8.3 Leveraging IoT and Smart Sensors for Real-Time Monitoring
IoT-enabled sensors provide real-time insights into production efficiency, equipment health, and inventory levels. Smart manufacturing systems collect data on machine performance, enabling predictive maintenance to prevent unplanned downtimes. Real-time inventory tracking, coupled with automated replenishment alerts, ensures JIT stock levels are maintained without manual intervention.
8.4 Integrating Automation and Robotics in JIT Systems
Robotics and automation enhance JIT by improving precision and efficiency. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) streamline material handling, reducing dependency on manual labor. Collaborative robots (cobots) enhance assembly line efficiency, minimizing human intervention while maintaining flexibility. Integrating robotics with AI-driven process optimization tools further refines JIT workflows, maximizing resource utilization.
9. Managing Risks and Challenges in JIT Implementation
9.1 Identifying Potential Disruptions in JIT Supply Chains
Just-in-Time (JIT) implementation hinges on precise coordination within the supply chain. However, disruptions such as supplier delays, geopolitical instability, natural disasters, and fluctuating market demands can destabilize operations. Identifying these vulnerabilities in advance allows businesses to mitigate risks before they impact production schedules and customer satisfaction.
9.2 Developing Contingency Plans for Unforeseen Events
A robust contingency plan is essential to counter unexpected supply chain disruptions. Organizations should diversify their supplier base, establish safety stock for critical components, and develop alternative logistics routes. Additionally, leveraging digital twins and predictive analytics can enhance resilience by simulating potential disruptions and identifying optimal response strategies.
9.3 Balancing Cost Savings with Operational Stability
While JIT aims to minimize excess inventory and reduce costs, an overemphasis on lean practices may render a business vulnerable to supply shortages. Striking a balance between cost efficiency and operational stability requires a strategic approach to inventory management, dynamic forecasting techniques, and close collaboration with suppliers to ensure just-in-time deliveries without jeopardizing production continuity.
9.4 Overcoming Resistance to Change in JIT Adoption
Employees, suppliers, and stakeholders may resist JIT adoption due to ingrained operational habits and fear of change. Effective change management involves clear communication of JIT benefits, comprehensive training programs, and active involvement of employees in the transition process. Addressing resistance with a structured approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement and smooth JIT integration.
10. Measuring JIT Success and Ensuring Continuous Improvement
10.1 Tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for JIT
Quantifying JIT effectiveness requires monitoring essential KPIs, such as inventory turnover rates, order fulfillment times, defect rates, and production lead times. These metrics provide actionable insights into JIT efficiency, enabling businesses to fine-tune their processes for optimal performance.
10.2 Conducting Regular Audits and Performance Reviews
Periodic audits and performance evaluations help identify inefficiencies, deviations from JIT principles, and areas for improvement. Conducting regular reviews ensures that JIT objectives align with organizational goals, and corrective actions can be taken promptly to enhance workflow efficiency.
10.3 Learning from Case Studies and Benchmarking Against Industry Leaders
Studying successful JIT implementations across various industries provides valuable lessons and best practices. Benchmarking against industry leaders allows organizations to adopt innovative techniques and refine their JIT strategies to achieve world-class efficiency.
10.4 Refining JIT Strategies for Long-Term Sustainability
Sustainability in JIT requires continuous adaptation to evolving market conditions, technological advancements, and regulatory changes. Businesses should remain agile, integrating cutting-edge innovations such as AI-driven analytics and automation to sustain JIT’s long-term success.
11. Future Trends in JIT and Lean Manufacturing
11.1 The Role of AI and Machine Learning in JIT Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing JIT by enabling predictive demand forecasting, automated inventory replenishment, and real-time supply chain analytics. These technologies enhance decision-making, mitigate risks, and optimize resource allocation.
11.2 Emerging Sustainable JIT Practices for Eco-Friendly Operations
Sustainability is increasingly shaping JIT strategies, with companies adopting green manufacturing techniques, minimizing waste generation, and reducing carbon footprints. Environmentally conscious JIT practices include energy-efficient production, circular economy principles, and sustainable supplier collaborations.
11.3 How Global Supply Chain Dynamics Influence JIT Adoption
The globalization of supply chains presents both opportunities and challenges for JIT implementation. Factors such as trade policies, regional economic shifts, and supply chain digitization impact the feasibility and effectiveness of JIT across different markets. Businesses must navigate these dynamics strategically to maintain a resilient and responsive JIT framework.
11.4 Preparing for the Future of JIT in an Evolving Business Landscape
As businesses face increasing complexity in supply chain management, the future of JIT will be shaped by digital transformation, automation, and strategic agility. Organizations must proactively embrace emerging technologies and innovative methodologies to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
12. Conclusion
Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing is a transformative approach that enhances efficiency, minimizes waste, and streamlines operations. However, successful JIT implementation requires meticulous planning, robust supplier relationships, and technological integration. By continuously refining JIT strategies, businesses can achieve sustainable growth, optimize resource utilization, and maintain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
13.1 What is Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing?
JIT is a production strategy that focuses on minimizing inventory and reducing waste by producing goods only as they are needed. It helps businesses optimize resource utilization and improve efficiency.
13.2 What are the main benefits of implementing JIT?
The key benefits of JIT include reduced inventory costs, improved production efficiency, lower waste levels, enhanced supplier relationships, and increased responsiveness to market demands.
13.3 What industries can benefit from JIT implementation?
JIT is widely used in manufacturing, retail, automotive, healthcare, food processing, and technology sectors. Any industry that requires efficient inventory management and streamlined production can benefit from JIT.
13.4 What are the biggest challenges of JIT implementation?
The main challenges include supply chain disruptions, dependency on reliable suppliers, workforce adaptability, resistance to change, and the need for accurate demand forecasting.
13.5 How can small businesses implement JIT successfully?
Small businesses can start by analyzing their inventory, working with dependable suppliers, implementing lean practices, training employees on JIT principles, and gradually reducing unnecessary stock.
13.6 How does JIT differ from traditional inventory management?
Traditional inventory management focuses on maintaining large stock levels to prevent shortages, while JIT aims to keep inventory levels as low as possible by producing and replenishing stock only when required.
13.7 How does JIT impact supplier relationships?
JIT requires businesses to develop strong partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide quick and flexible deliveries to maintain seamless operations.
13.8 Can JIT be used alongside other lean manufacturing techniques?
Yes, JIT can be integrated with methodologies like Six Sigma, Kaizen, and Total Quality Management (TQM) to enhance overall operational efficiency and quality control.
13.9 What role does technology play in JIT implementation?
Technology such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Internet of Things (IoT), and predictive analytics help businesses track inventory in real-time, optimize production schedules, and improve demand forecasting.
13.10 What are some examples of companies that use JIT successfully?
Toyota, Dell, McDonald’s, and Harley-Davidson are some of the companies that have successfully implemented JIT to streamline operations and reduce costs.


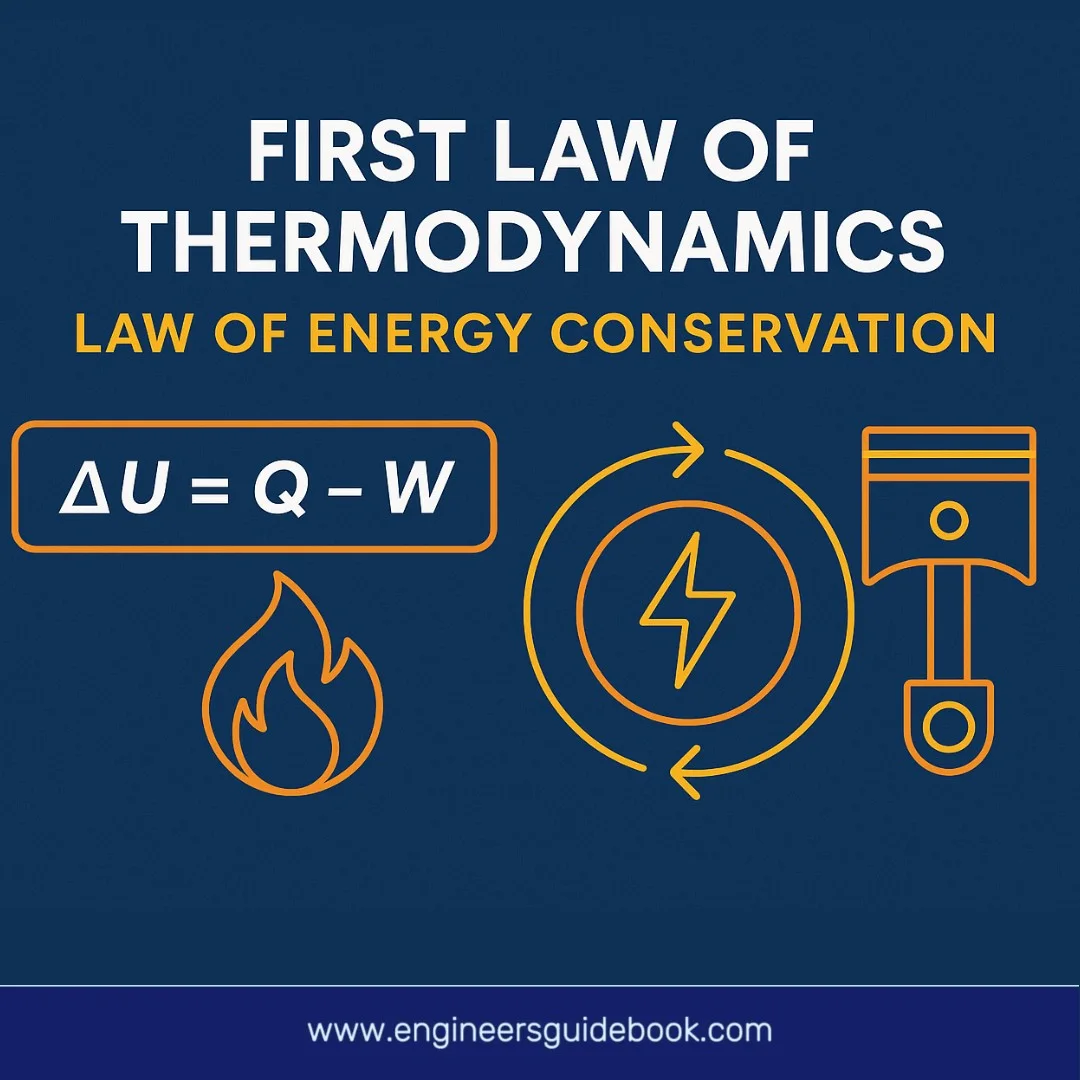
2 Responses
Currently it appears like WordPress is the top blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?